Introduction
OLFM stands for Oracle Lease and Finance Management. It has also been known as OKL (Oracle Contract for Lease) and OLM (Oracle Lease Management) earlier. This product was developed as a software solution for Equipment Leasing industry.
OLFM is part of the Oracle’s eBusiness Suite and fully integrated with it. It was developed on the technical foundation of Oracle Core Contracts, along with other products like Service Contract, Royalty Contracts, Sale Contracts etc.
First Release of OLFM was done sometime in 2001 with 11.5.8. The latest release is R12.2.x and has the same technology stack (OA Framework) as other products of Oracle.
OLFM Customers
OLFM was developed on the requirement of GE Capital where it was first implemented. Later on lot of other customers have implemented this product. Customer partial list is given below:
- CaterPillar
- John Deere
- Canon
- Navistar
- DLL
- NeoPost
- Cisco
- Key Bank
- GE Capital
- Beckman Coulter
- SunRun
- Ricoh
- Macquarie
Integration with Other Modules
OLFM is a solution for Equipment Leasing Industry. It is part of the Oracle’s eBusiness Suite and is integrated with it. OLFM needs the following mandatory modules to work:
• Receivables
• Payables
• General Ledger
• Fixed Assets
• EBiz Taxes
• SLA (Sub-Ledger Architecture)
This means that when implementing OLFM, we also need to implement the above modules fully. In addition to the above modules, we need partial implementation of the following modules:
• CRM Foundation
• Inventory
• Order Management
• Collections (if delinquency is to be handled through Oracle)
• Installed Base
• Service Contracts (if we use service with Leasing)
• Core Contracts
Receivables: OLFM generates billing and transfers to Receivables module. The billing may be for contractual payments, ad-hoc invoices, late charges, termination proceeds etc. Once transferred to Receivables, the invoice is created, printed and managed by Receivable module.
Payables: OLFM generates funding and disbursement transactions and transfers the details to payable modules. In payable module, the payable invoices are handled and paid to the vendor/service providers.
Fixed Assets: When an equipment is leased, the entry is created in Fixed Asset module where it may be depreciated. The cost of the asset is records in Corporate and Tax Books. Any adjustment done in OLFM is automatically reflected in Fixed Asset Module.
General Ledger: All accounting done (in OLFM or other modules) is transferred to General Ledger (through SLA Module).
SLA: The accounting is transferred from sub-ledgers to General Ledger through SLA module.
EBiz Taxes: This tax module of Oracle is used for deriving tax rates for transactions. Many customers integrate eBiz Tax module with vertex or sabrix third party software to get the tax rates. If the tax requirements are simple, then only eBiz tax can be used.
Different type of Leases
OLFM can be used to handle any kind of Lease and Loans. Some of the popular form of leases prevailing in the leasing industry are described below:
Operating Lease: A lease whose total term is much less than the useful life of the asset is classified as operating lease. An operating lease should not meet any of the criteria listed for direct finance lease. The equipment leased through operating lease have large residual at the end of the lease term. The equipment ownership remains with Lessor who takes depreciation benefits too.
Operating leases rental payments are recorded as expenses in lessee’s books, whereas rental payment received are shown as income in lessor’s books.
Finance Lease: A lease is considered Direct Finance Lease if it meets any of the following criteria:
- The life of the lease is 75% or greater of the asset’s useful life.
- The title should be transferred to Lessee at the end of the lease period.
- There should be a bargain purchase option, much below the market value, at the end of the lease period.
- The present value of the rental payments should be at least 90% of the original equipment cost.
In Finance Lease, depreciation benefits are taken by lessee and thus asset is not depreciated in lessor’s books.
TRAC Lease: TRAC (Terminal Rental Adjustment Clause) lease combines the advantage of leasing while retaining the option to purchase the equipment at the end of the lease term at pre-determined residual value. Monthly payments can be adjusted based on the residual value determined. If higher residual value is selected, the monthly payments can be reduced or vice-versa. These kind of leases are usually used in Vehicle leasing industry.
Hire Purchase: It is similar to finance lease and the term is used in UK and European countries.
Loans (Fixed and Variable Rates): In many situations, it is preferable for the lessor to provide loans instead of a lease for equipment finance. The difference between a Lease and Loan are given in the following table:
Some important Leasing Terms
Net Present Value(NPV): It is the discounted value of the future cash flows, discounted by a specified discount rate. The formula for calculating NPV is as follows:
NPV = Amount / (1 + r)**n
Where r is monthly interest rate
N is the period of the cash flow
** represents exponential
Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The rate at which sum of the present value of all cash flows (including the cash outflow in zeroth period) becomes zero.
Period 0 1 2 3 4
Cash Flow -50000 6000 6000 6000 6000
NPV -50000/(1+r)**0 + 6000/(1+r)**1 + 6000/(1+r)**2 + 6000/(1+r)**3 + 6000/(1+r)**4
In the above example, the value of r for which the sum of all NPV becomes zero is called IRR.
Gross Receivables: Some of all the future cash flows which would be paid by lessee as Rental
Lease Income: Gross Receivables – (Sum of Present Value of all positive cash flows)
Amortization: An act of recognizing an income or expense over a period of time, as against recognizing immediately on receipt/expense.
Depreciation: An equipment when used loses its economic value. This reduction in value is termed as depreciation. Usually, value of equipment divided by useful life of equipment (in months) is termed as monthly depreciation.
Residual: Value of an asset left after the contract term is complete.
Initial Direct Cost (IDC): It is the amount spent by lessors in acquiring the deal. It is mostly represented as percentage of the financed amount. This amount is usually amortized over the life of contract.
Some Key Concepts of OLFM
In order to understand the OLFM product, we need to understand some of the key concepts and terminology used in describing the product.
Financial Product: The type of lease provided by lessor is modelled as a Financial Product. For example, a lessor may be providing finance lease, loans, operating lease etc. Each of this lease type is created as a separate product.
Transaction Type: For a lease contract, any activity done is recorded as a transaction type. For example, act of booking a contract, making a change to booked contract, termination etc. are example of activities done on a contract. Each of this is termed as transaction type. A transaction type may have an accounting impact (means some accounting needs to be done whenever that transaction occurs).
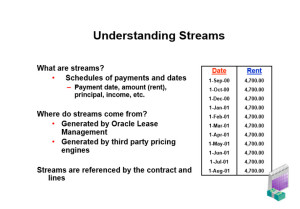
Stream Type: In any lease contract, we have different kind of cash flows. We charge rent to customers, charge some fees, fund vendors, do amortization of certain expenses. All such cash flows are recorded as stream types. So stream type is name given to cash flow used for billing or accounting purpose.
Formula Engine: In order to provide flexibility to derive amounts based on custom logic, OLFM has developed a feature of formula engine. The formulas can be created based on custom requirements with amount derived using PL/SQL code.
Super Trump: It is a third party tool provided by Ivory software, which is used for pricing of the leases. OLFM is integrated with super trump to generate streams and derive yields.
Rules and Rule Groups: This is a technical architecture which was developed in Core contract module and is being used in OLFM to capture unstructured contract data.
Lease Management Responsibilities
Lease Super User: This responsibility is used to carry out most of the tasks in OLFM. It shows the screens in HTML format (OA Framework pages). All the setups and operations are available in this responsibility.
Lease Administrator: This is Oracle forms based responsibility and is used to run batch programs/concurrent programs.
Lease center Agent: This responsibility is Oracle Forms based responsibility and is used by customer service representative to answer the customer queries.
Self Service Feature
A Customer or vendor can be setup to access the details of the contracts over the web using OLFM’s self- service feature. This allows a customer or vendor to access the details of contracts, assets and invoices. A customer can also make request for Termination quote, renewal quote over the web using this feature.
Overview of a Lease Contract
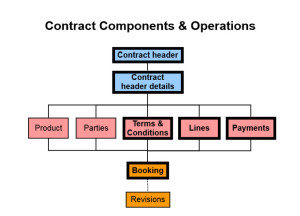
A Lease contract can be described by describing its different components:
a. Lease Header
This part of contract contains contract level information like start date, end date, term, financial product, customer name and account number.
b. Parties
All parties on the contract are created here. System automatically creates lessor and lessee, other parties like vendor, insurance provider, Guarantor can be added.
c. Terms and Conditions (T&C)
All terms and conditions related to the contract are captured here. Oracle provides many standard T&C like billing setup, termination process, termination quote calculation etc. It is possible to add custom T&C based on custom requirements. These T&C are used throughout the life of the contract to determine how contract is administered.
d. Financial Assets
All equipment which are being leased can be added here. If the equipment is serialized, then you need to enter a serial number. An equipment can contain one unit or multiple units. Before adding equipments here, the equipments are created as inventory items in Oracle inventory module. It is also possible to add add-on to the equipment, like a GPS unit to a vehicle equipment. The add-on unit adds to the cost of the main equipment but is not created as an asset in Fixed Asset module.
For the equipment, we need to enter cost, useful life, depreciation method, make, manufacturer etc. These pieces of information flow to the Fixed asset module on contract activation.
e. Fees (income and Expense)
There could be many kind of fees on the contract. Some fees could be expense to the lessor (like initial direct cost, dealer commission). Some fees could be income to the lessor (like documentation fees). These fees can be recognized immediately or could be amortized over the life of the contract.
It is also possible to finance the fees, in which case the financed amount increases. For example, upfront tax levied on lease equipment could be financed by lessor. Similarly, any insurance provided by the lessor could be financed.
In this section we also add any service and maintenance fees for the service provided on the equipment. If the service is provided by a third party, then it is possible to setup a pass-thru of the billing amount received to the third party.
f. Payment Definition
In this section contractual payments for asset, service and fees are defined. Before defining payments, the corresponding assets, service and fees should have already been defined. The payments could have simple structure or could have any complex structure, with gaps and payment holidays. The payment can be charged in advance (beginning of periods) or arrears (end of the period).
These payments defined along with the cost of asset determine the overall profitability (IRR) of the lease contract.
g. Insurance
As per law, the leased equipment must be insured for suitable amount. The insurance can be obtained by lessee from a third party (called Third Party Insurance) or it could be provided by Lessor. OLFM has a full-fledged functionality for lessor to provide insurance (in association with an insurance provider). For some of the lessor, the commission received for providing insurance forms a substantial part of the profits. The amount received for insurance from lessee can be automatically disbursed to the insurance provider after deducting the lessor commission.
h. Subsidies
OLFM provides functionality to implement subsidy which is provided by the manufacturer/vendor to increase the sale. This subsidy could be in the form of Rate subsidy or the Discount subsidy. In rate subsidy, the interest rate charged to the lessee is reduced (and this is in turn billed to the vendor/manufacturer by the lessor). In discount subsidy, the asset acquisition cost is reduced (and the benefit is passed to the lessee).
Subsidies help in increasing the sale of equipments without decreasing the equipment price.
i. Security Deposit
Sometime lessors require certain amount from lessee to hold as security deposit. Usually security deposit is taken in terms of n number of months’ equivalent rent, for example, 2 or 3 months equivalent of Rent. This amount is held till maturity of lease and can either be adjusted in the last month’s rent or could be adjusted against termination quote.
j. Down Payment
Most lessors need certain amount of down-payment from the lessee. Down-payment reduces the financed amount and thus reduces the financial risk to the lessor.
k. Interim Rent
When the equipment delivery to the lessee is before the contract start date, an interim rent is charged. For example, an equipment is delivered on 2nd Nov to the lessee but the payment starts only on 01st of Dec. In such cases, lessor would charge the pro-rated rental amount from 02nd Nov to 01 of Dec.
Contract Authoring Process
a. Creating a Contract
In OLFM, a contract can be created through multiple channels. These channels are:
– Manual creation
– Copying an existing contract
– From contract template
– From Lease Open Interface
– From Lease Quote
In most of the implementation, contract is created using the Lease Open interface. Contract is originated in a legacy system and then interfaced to OLFM. To reduce the need to provide large amount of repeating data, a contract template is created in the OLFM system and referred in the interface. OLFM then defaults most of the values from contract template.
b. QA Check
After contract is created, it passes through Quality Checks. These quality checks insure that data entered is correct and consistent. Quality Assurance is done through a QA Check list, which has some standard processes (provided by Oracle) and can have custom defined processes. A QA process can be set to Error or Warning; In case of error, system would not allow you to activate contract till the error is fixed. In case of warning, you can proceed further without correcting the error.
QA Checks are defined in OKC module against the QA Check list ‘OKL LA QA CHECK LIST’.
c. Pricing (Stream Generation)
After a contract passes QA Check, it goes through Pricing process. The pricing process generates streams based on the payments defined. The pricing can be done either through internal stream generation process (provided by Oracle) or through External Pricing Engine (Super-Trump). Usually when lease payments are complex, an external pricing engine is used (which requires buying a license from Ivory Software).
The pricing process generates streams for payments and accounting. These streams are then used for billing and accrual purpose.
d. Approval
After pricing, contract may pass through approval process. It is possible to bypass this stage by setting appropriate profile option. If approval is required, then it is done through a workflow process which uses Oracle’s Approval Management module. It is possible to configure the Approval Management Process to define any complex approval process.
e. Activation
After approval, contract is activated. The activation process creates a Booking transaction in the system. It also creates asset in Oracle Fixed Asset (for Leases, Loans do not create FA Asset). The serial number and install address information is passed to Oracle Installed Base where an Installed Base instance is created.
Once contract is activated, it cannot be modified. For most modifications, it has to go through Rebook (Revision) process.
Taxes
Lease attract a transaction tax based on location of the asset. There are different tax rates based on the state, city and county. Overall, the tax can be levied in the following way:
Upfront Tax: In this case, the tax is collected upfront (at the beginning of the lease). The tax calculation can be on the basis of Gross Receivable or the Equipment Cost.
Tax on Stream: In this case, the tax is collected on the rental amount on periodic basis.
OLFM is able to handle both kind of taxes. When the tax is upfront, a tax invoice is created immediately on contract activation. When the tax is on the stream, tax is calculated on the invoice when it is created in AR.
OLFM also provides facility to finance the upfront tax. For tax financing, payment needs to be defined to recover the financed tax from the lessee.
OLFM is fully integrated with the eBiz Tax module to derive the taxes. eBiz module in turn may be integrated with a third party software like Sabrix and Vertex to get the exact current tax rates depending on the installation location.
Contract Changes
Rebook
Once a contract is booked, any changes to it can be carried out by Rebook/Revision process. Any change which does not have any financial impact (like changing Billing Setup, Equipment Serial number/make etc.) can be carried out from Lease Center without a need to do the Rebook.
Any of the following changes would need a rebook:
• Cash Flow Dates
• Rents
• Asset Values
• Depreciation Values
• Book Classification
The rebook process creates a copy of the original contract, where you can make the required changes and carry the contract all the way from QA Check, Pricing, Approval and Booking. On activation of Revision contract, the changes are copied to the original contract and the copy contract is abandoned.
Rebook process does now allow change in Customer Name or the Financial Product. For doing this type of change, we need to follow another process (Transfer and Assumption).
Transfer and Assumption (T&A)
This is a process of revision where changes are made to contract for the following:
- Customer Change
- Financial Product Change
Customer change is required when the leased equipment is transferred to another customer or when a company is merged with another company and thus billing has to be done to new entity.
T&A Process starts by creating a request in Lease Center, approving it and then carrying out the changes in Lease Super User responsibility. This process will terminate the old contract and create a new contract from the T&A effective date. The new contract will have a new contract number.
Cash Management
Billing
Billing is a process of creating invoices for the rental and service and sending invoices to the customer. Bill can be generated on due date or any number of days in advance (decided by Print Lead Days). Billing is generated in OLFM and transferred to Receivable module where it is created as Receivable invoice and sent to the customer.
OLFM Billing program is used to bill the following kind of dues:
- Contractual Payments Payments defined in the contract such as Rent, Fee and Service
- Event Based Payments Payments such a rebook adjustment, Quote Fees, Contract Obligations for termination.
- Policy Based Payments such as Late Charge and Late Interest, Ever-Green Billing.
- Manual Manual Ad hoc invoices.
- Investor Agreement Invoicing the investors for their stake in investor Agreement
- Taxes Property tax and upfront tax.
Billing is initiated in OLFM by running concurrent programs which bills the dues in OLFM and transfers data to AR Module. Invoices can be grouped together by creating a setup in OLFM, which can group multiple contracts, multiple fee lines etc. together for better presentation to the customer.
Funding Process
Funding is a process of making payments to vendor who supplied the equipments. OLFM provides the following kind of funding:
• Asset Funding: Making payments for equipment supplied. Maximum funding possible under this category is equal to the cost of all the assets.
• Expense Funding: Making payments for the dealer/vendor expenses. These expenses should have already been defined as fees in the contract authoring.
• Manual Disbursement: Any other expense to be paid to vendor which is not associated to any asset.
• Pre-Funding: Funding before the contract is activated. Sometime vendor requires an amount to be paid before they supply the equipment.
• Supplier Retention:
After funding request is created and approved, it is transferred to payable module where it becomes AP invoice. From there, the payment can be made to the vendor.
Receipts Management
Receipts can be done in multiple ways:
a. Direct Debit
b. ACH
c. Credit Cards
d. Lock-Box
e. Check
f. Cash
The receipts are applied to outstanding invoices using Cash Application Rules.
Cash Application Rules
Cash application rules determine how the given cash is applied on the outstanding invoices. For example, you may want to apply the cash first to Rent, followed by Fees, followed by Taxes. Customer can have any kind of cash application rules and the system will apply the given cash using the preference indicated.
Disbursement
Disbursement is a process of payment to vendors/ third parties for the services rendered by them. For example, any service and maintenance charges collected by lessors need to be disbursed to service providers. Similarly, any amount collected for lease insurance need to be disbursed to the lease insurance provider company.
Disbursement feature is also used to pay to the investors for their stake in Investor Agreements.
For service provided by the third parties, the disbursement terms and conditions are setup at the contract level as pass-thru. In this setup, we specify vendor and vendor sites, payment terms, disbursement event, percentage of the amount to pass-thru etc.
When billing is done or receipt happens for the amount, the disbursement program can pick up these amounts and create payable invoices to be paid to vendor/service providers.
Similarly, for investor agreements, disbursement is done when billing for the securitized contract is complete (or amount is received from customer).
Disbursement is initiated by running a set of concurrent programs which collects the required information from OLFM and transfers the amount to Payable modules where they become payable invoices and payment is made from there.
Revenue Management
Accrual
Accrual is a process of recognizing revenue/expense for the contract. In lease contracts, the revenue or expense is not recognized immediately since payment happens over a series of cash flows for long duration. Thus revenue recognition is done over the full life of the contract.
Finance Lease
Lease Income: For finance leases, lease income is computed at the beginning of the lease and this lease income is recognized over the life of contract
Residual Accretion: In certain situations, residual income receivable at the end of the lease is accrued over the life of the contract for Finance Lease.
Operating Lease
Rental Accrual: The income for operating lease is the rent received on periodic basis. This rent amount is accrued as income.
Depreciation Expense: The depreciation is difference between the asset cost and residual value. This amount is divided by lease term to arrive at the monthly depreciation expense. This expense is accrued over the life of the contract.
Loans
Interest Accrual: For the contracts of type loans, the accrual amount is equal to the interest amount for the period. This amount is accrued over the life of the loan.
Initial Direct Cost (IDC): This amount is certain percentage of the financed amount. This amount is amortized over the life of the contract. IDC is accrued for Operating lease, Finance Lease and Loans.
In OLFM, the streams to be accrued are associated with financial product. The amortization of the streams is created by super-trump or internal stream generation process. The streams associated with the financial product are then accrued by the Accrual concurrent program.
Accrual Rules
Streams can be associated with the accrual rules. These accrual rules decide when the accrual should be stopped. For example, when certain number of invoices are not paid or a certain invoice is overdue for a number of months, the accrual can be stopped.
Accrual rules also specify when to re-start the accrual after the accrual process has stopped.
Accounting
In OLFM, there are two ways to do the accounting:
• Accounting using Accounting Templates
• Accounting using Accounting Method Builder
When accounting is done using accounting templates, the templates are created for each financial product for combination of transaction type and stream types. Each template contains two accounting lines, debit line and credit line with the associated accounts.
For Booking, Rebook, Termination and Transfer & Assumption, we need to associate a formula with the accounting template. This formula is used to derive the amount to be accounted. For other transaction types, formula is not required and amount is taken from the streams generated.
When accounting method builder is used for accounting, the accounting definition is taken from account derivation rules defined in SLA module. This method of accounting provides lot of flexibility in defining the accounting rules and require less data entry, as against accounting template method.
Once accounting method builder is chosen as accounting method, it cannot be changed back to accounting templates.
For the billing and disbursement, the derived journals are transferred to General ledger from the respective modules. For example, any invoice accounting done will be transferred to GL from AR directly. However, accounting generated in OLFM for Booking, Rebook, Termination and Transfer & Assumption transactions is moved to GL directly from OLFM.
End of Term Options
When contract matures, the following possibilities arise:
• Contract is Renewed
• Contract is Terminated with Purchase of Equipments
• Contract is Terminated without Purchase of Equipments
• Contract is extended Indefinitely (Evergreen)
Contract Terminations
Contract can be terminated early or at the end of the lease. So there are two kind of terminations possible:
• Early Termination
• End of Term Termination
Termination can be partial or full. In partial termination, only some of the asset lines are terminated while in full termination all the assets are terminated.
• Partial Termination
• Full Termination
Termination may be with or without purchase. When termination is done without purchase, the asset is returned to the lessor. In case of with-purchase termination, asset remains with the lessee and lessor charges purchase amount.
• Termination with Purchase
• Termination without Purchase
Termination is initiated with creation of a termination quote. The termination quote can automatically derive the contract obligation from terms and conditions setup on the contract. Some of these amounts can be overridden by the user.
If a manual quote is created, then amounts are not derived from the terms and conditions. In this case, the amounts can be manually entered by the user.
• Automatic Quote
• Manual Quote
Termination Quote follows the following process:
• Quote Creation (Draft Status)
• Quote Approval (Approved Status)
• Quote Acceptance (Accepted Status)
• Quote Completion (Complete Status)
Quote creation process creates various amounts from terms and conditions on the contract. These amounts can be modified by the user. Then the quote is sent for approval. After quote is approved, it can be accepted. On acceptance of a quote, a workflow is launched. This workflow creates all the termination invoices, creates termination transaction (which is later accounted), and terminates the asset/contract.
When a partial termination quote is accepted, only partial number of assets are terminated but the contract remains in the Booked status. In this case, the contract is automatically rebooked with the remaining active assets.
Evergreen
When contract is eligible to go to evergreen (as per terms and conditions), the contract is moved to Evergreen status (unless it is terminated earlier). In evergreen, contract has no fixed end date. The contract is billed month-to-month with the rental amount equal to the last month’s rent of the active period.
When contract is eligible for evergreen, its status is changed to EVERGREEN by a concurrent program. A separate concurrent program is run for creating billing every month. At a time, one month’s billing is created and sent to the customer. This arrangement continues until the lessee wishes to terminate the contract or want to renew the contract for a fixed period of time.
Asset Management
When contract is terminated with return of the assets (without purchase), the equipment comes back to the lessor. Asset is also returned when it is repossessed. The returned equipment goes through inspection process and the lessor can do one of the following:
• Re-Lease the Asset
• Sale the Asset
• Scrap the Asset
On asset return, asset is inspected and any repair required is estimated. The repair cost may be charged to the lessee. In addition, a lessor may charge the following fee for asset returns:
• Auction Fee
• Marketing Fee
• Miscellaneous Fee
• Repossession Fee
• Scrapping Fee
• Shipping Fee
The return functionality also provides a facility to update the asset cost and other depreciation parameters. These updates are written back to FA Module.
Re-lease
Re-lease is a process of Re-leasing an asset which has come off-lease. To Re-Lease an asset, the asset return status has to be updated with status ‘Available for Re-Lease’.
During contract authoring, the assets having the status ‘Available for Re-Lease’ will be available for selection. The re-leased asset will retain the same asset number and serial number in the new contract. A contract can be created having both new and re-leased assets.
Rollover
Rollover is a process where existing contract is terminated and termination proceeds is financed through a new contract. A termination quote with rollover is created and approved. A new contract is created for the same customer and bill to address and the rollover quote is referenced in the financed fee section. The rollover amount comes in the new contract as financed fee.
Repossession
Repossession is an act of retrieving equipment from a lessee either forcefully or voluntarily. When a loan gets delinquent, repossession is initiated. The repossession is supported by OLFM’s termination quote functionality.
The repossession works as follows:
a. Create a manual quote for repossession
b. Update the amounts
c. Send quote for approval. When quote is approved, an asset return request is automatically created.
d. Accept the Quote. Before accepting the quote, the asset return request status should be set to ‘Asset Repossessed’. That means quote can be accepted only when asset is already repossessed.
e. The acceptance will trigger a workflow which will terminate the contract and asset will be created in FA.
f. The asset cost can be manually adjusted in FA and then asset can be re-leased, sold, or scrapped.
Customer Service
OLFM provides a customer service functionality which can be used by customer service representative to answer any query the customer may have. This is an Oracle Forms based user interface where a contract can be queried on various parameters.
The screens show contract overview, billing details, party details, insurance details, receipt details, asset details etc.
This user interface is also used for many other functionalities like requesting a Transfer and Assumption, creating a credit memo on existing invoice, processing a pre-payment of loans.
There is a feature of Fulfillment letter available in lease center, where letters can be generated and sent to customers. These letters are designed and generated using Oracle’s XML Publisher technology.